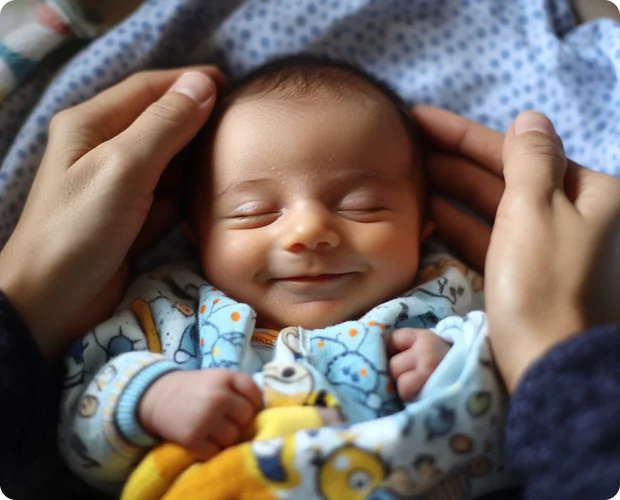
The prolactin hormone plays a crucial role in regulating various reproductive functions in both men and women. Maintaining optimal prolactin levels is essential for ensuring fertility and overall reproductive health. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how prolactin hormone levels can impact fertility in both genders.
Also read: Role of Hormones in Fertility
How Prolactin Hormone Levels Affect Fertility in Men and Women
Prolactin, a hormone the pituitary gland produces, is primarily known for stimulating breast milk production during pregnancy and after childbirth. However, its functions extend beyond lactation and have significant implications for fertility. Abnormally high or low prolactin levels can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance required for successful conception and healthy reproductive function. Understanding the intricate relationship between prolactin and fertility is crucial for people seeking to conceive or maintain optimal reproductive health.
Let’s explore the role of prolactin in fertility, understand normal prolactin levels, discuss the causes of abnormal levels, and examine the effects of high or low prolactin on male and female fertility.
Also read: Does Female Masturbation Cause Hormonal Imbalance
What is the Role of Prolactin in Fertility
Prolactin plays a multifaceted role in fertility for both men and women, including:
- In women, prolactin regulates the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and progesterone production, a hormone essential for maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
- In men, prolactin influences testosterone production, sperm development, and sexual function.
- While prolactin is necessary for reproductive health, excessive or deficient levels can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance, leading to fertility issues.
Understanding Normal Prolactin Levels
Female Prolactin Levels:
Normal prolactin levels in non-pregnant females typically range from 5 to 25 ng/mL (nanograms per millilitre). However, these levels can fluctuate during different phases of the menstrual cycle, with a slight increase happening during the luteal phase (the second half of the cycle).
During pregnancy, prolactin levels rise significantly to prepare the body for lactation. After childbirth, prolactin levels remain elevated to support breastfeeding. Once breastfeeding is discontinued, prolactin levels gradually return to their normal, non-pregnant range.
Prolactin in Men:
Normal prolactin levels in men range from 4 to 15 ng/mL. Unlike women, men’s prolactin levels do not fluctuate significantly throughout their lives unless there are underlying medical conditions or external factors influencing the hormone’s production.
Also read: Male Hypogonadism: Treatment of Low Testosterone
Causes of High or Low Prolactin Levels
Several factors can contribute to abnormal prolactin levels in both men and women. Understanding these causes is essential for identifying and addressing potential fertility issues.
High prolactin levels (hyperprolactinemia) can be caused by:
- Pituitary tumors (prolactinomas)
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid)
- Certain medications- antipsychotics, antidepressants, blood pressure medications
- Chronic kidney disease
- Compression of the pituitary stalk (e.g., due to a tumour or injury)
- Excessive stress or physical strain
Low prolactin levels (hypoprolactinemia) can result from:
- Pituitary gland disorders or damage
- Certain medications- dopamine agonists, opioids
- Excessive exercise or physical activity
- Severe malnutrition or eating disorders
- Genetic disorders affecting the pituitary gland
Also read: The Role Of Hormonal Imbalances In Female Infertility
Effects of Abnormal Prolactin Hormone Levels in Men
Abnormal prolactin levels can have various effects on male fertility and overall reproductive health.
Impact on Testosterone Production:
High prolactin levels can suppress the production of testosterone. Low testosterone hormone levels can result in erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and infertility.
Effects on Sperm Production:
Elevated prolactin levels can impair sperm production (spermatogenesis) by interfering with the hormonal signals required for normal sperm development and maturation. This can result in decreased sperm motility, reduced sperm count, and abnormal sperm morphology, all of which can contribute to male infertility.
Potential for Gynecomastia:
In men, high prolactin levels can stimulate the growth of breast tissue, leading to a condition called gynecomastia (enlarged male breasts).
Impact on Sexual Function:
High prolactin levels can affect sexual function in men, such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and difficulties achieving orgasm. Conversely, low prolactin levels may also contribute to sexual dysfunction and reduced fertility.
Influence on Mood and Mental Health:
High levels of prolactin may result in increased anxiety, depression, and irritability, which can indirectly impact fertility by affecting overall well-being and sexual function.
Disruption of Normal Erectile Function:
Increased prolactin levels can interfere with the normal physiological processes necessary for achieving and maintaining an erection. This can result in erectile dysfunction, which can significantly impact sexual function and fertility.
Effects of Prolactin Hormone Levels in Females
In women, abnormal prolactin levels can have various effects on fertility and reproductive health.
Impact on Menstrual Cycle Regularity:
High prolactin levels in non-pregnant females can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle, leading to irregular or absent periods (amenorrhea). This inconsistency in the menstrual cycle can make it difficult to predict the time of ovulation and potentially reduce the chances of conception.
Effects on Sexual Function and Libido:
Elevated prolactin levels have been associated with decreased libido and sexual desire in women.
Disruption of Ovulation:
Abnormally high prolactin levels in non-pregnant females can interfere with the hormonal signals necessary for ovulation, the process of releasing a mature egg from the ovary. This can lead to anovulatory cycles, which can significantly reduce fertility.
Impact on Hormonal Balance:
Abnormal prolactin levels can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance (estrogen and progesterone) necessary for fertility, potentially leading to fertility issues and other reproductive health problems.
Effects on Fertility Treatments:
High prolactin levels can negatively impact the success of fertility treatments. Elevated prolactin levels can interfere with the body’s response to fertility medications and reduce the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
Effects on Luteal Phase Function:
The luteal phase is the latter part of the menstrual cycle, during which the body prepares for potential pregnancy. High prolactin levels in non-pregnant females can disrupt the normal function of the luteal phase, potentially leading to issues with implantation and early pregnancy loss.
Managing Abnormal Prolactin Levels
Addressing abnormal prolactin levels is crucial for improving fertility and overall reproductive health. Several treatment approaches and lifestyle modifications can help manage prolactin levels, including:
- Medication:
- Doctors commonly prescribe dopamine agonists to lower prolactin levels in cases of hyperprolactinemia.
- In some cases, treating the underlying cause (e.g., pituitary tumour, hypothyroidism) may help normalise prolactin levels.
2. Surgery:
-
- In cases of prolactinomas (pituitary tumours producing excess prolactin), doctors may recommend surgical removal if medications are ineffective or the tumour is large and causing significant symptoms.
3. Radiation therapy:
-
- In some prolactinomas, radiation therapy may aid in shrinking the tumour and reducing prolactin production.
4. Hormone replacement therapy:
-
- For cases of hypoprolactinemia (low prolactin levels), doctors may prescribe hormone replacement therapy to restore normal prolactin levels and support fertility.
5. Lifestyle Factors Influencing Prolactin Levels:
-
- Certain lifestyle modifications can help manage prolactin levels and support overall reproductive health. These include stress management, nipple stimulation, good quality sleep (particularly early morning sleep), optimal body weight, and moderate and regular exercise.
6. Dietary Changes and Habits:
-
- A balanced diet enriched in essential vitamins and nutrients, such as vitamins B6 and E, zinc, and selenium, may help regulate prolactin levels. In addition, managing stress through practices like yoga, meditation, or counselling can positively impact prolactin levels and overall fertility.
7. Reduce Consumption of Caffeine and Alcohol:
-
- Excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeinated beverages has been linked to increased prolactin levels. Limiting or avoiding these substances can help maintain a healthy hormonal balance.
Prolactin Level Test
If you suspect abnormal prolactin levels or are experiencing fertility issues, consult with a doctor. They may recommend a prolactin level test, which involves a simple blood analysis to measure the prolactin concentration in your body.
Regular monitoring of prolactin levels can help identify potential imbalances and guide appropriate treatment strategies to support fertility and reproductive health.
Conclusion
The prolactin hormone plays a crucial role in regulating fertility in both men and women. Maintaining optimal prolactin levels ensures successful conception, healthy pregnancy, and reproductive function.
Abnormal prolactin levels can have various effects, including disrupted menstrual cycles, ovulation problems, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and reduced sperm production. Understanding the causes of high prolactin and its effects is vital for individuals seeking to conceive or maintain optimal reproductive health.