The process of pregnancy and embryonic development is complex and delicate. Fetal growth is an exponential process and is influenced by uteroplacental, dietary, genetic, and fetal factors. It starts before you are even aware that you are pregnant and concludes after your baby is born. Infections, inflammation, the dietary and metabolic environment, social determinants, and genetics all have an immediate impact on the fetus’s development in utero as well as long-term programming into childhood and adulthood. It is crucial to understand these elements in order to prevent developmental problems and encourage healthy pregnancies.
Also Read: The Four Stages of Embryonic Development
Overview of Fetal Development in the First Trimester
Fetal development typically follows a predictable course. Conception usually happens approximately two weeks after your last period begins. The fetus is most vulnerable during the first 12 weeks. During this time, all of the major organs and bodily systems are developing and can be damaged if the fetus is exposed to infectious agents, drugs, radiation, specific medications, tobacco, or toxic substances.
Key Milestones in the Development of the Embryo and Fetus
The sperm and egg combine in any one of your fallopian tubes to form a one-celled entity known as a zygote. The zygote normally contains 46 chromosomes, 23 from the biological father and 23 from the biological mother. These chromosomes help establish your baby’s gender and physical characteristics. Soon after fertilization, the zygote moves down the fallopian tube to the uterus. The rapidly dividing ball of cells, known as a blastocyst, has begun to burrow into the uterine lining (endometrium). This process is known as implantation. The embryo will develop from the blastocyst’s inner clump of cells. The outer layer will give rise to a portion of the placenta, which will nourish your baby throughout the pregnancy.
Also Read: From Cell to Life: The Path from Zygote to Baby
Brain Development in Fetus During Early Pregnancy
During early pregnancy and embryonic development, fetal brain development in the fetus begins with the formation of the neural tube, which ultimately gives rise to the brain and spinal cord. By the fifth week, important structures like the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain begin to differentiate, providing the foundation for the central nervous system. Proper brain development in a fetus at this stage is influenced by genetic variables, maternal nutrition (particularly folic acid), and the lack of hazardous exposures, stressing the necessity of a healthy environment.
1st Trimester Fetal Development: A Week-by-Week Guide
Pregnancy and fetal development occur in a meticulous way, and the following are the stages of fetal development during the first trimester:
| TIMING | STAGES OF FETAL DEVELOPMENT |
| Week 1 and 2 | Conception |
| Week 3 | Fertilization |
| Week 4 | Implantation |
| Week 5 | Hormone levels increase |
| Week 6 | Neural tube closes (Brain and spinal cord) |
| Week 7 | Baby’s head develops |
| Week 8 | Baby’s nose forms |
| Week 9 | Baby’s toes appear |
| Week 10 | Baby’s elbows bend |
| Week 11 | Baby’s genitals develop |
| Week 12 | Baby’s fingernails form |
Genetic Factors Affecting Embryonic Development
Embryonic fetal development is a significant predictor of health and disease in both childhood and adulthood. Fetal growth is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors, such as fetal and parental variants in genes, maternal nutrition, and placental function.
Chromosomal Abnormalities
Chromosomal abnormalities result from defects in the number or structure of chromosomes, which have a substantial impact on embryonic development. Common trisomies include Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13), all of which can cause developmental delays, physical deformities, and other health issues.
The Role of Parental Genetics
Parental genetics play an important role in embryonic and fetal development since the fetus receives half of its genetic material from each parent. These genetic instructions govern physical characteristics, organ development, and the likelihood of hereditary disorders. Mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, or hereditary illnesses from either parent can have a substantial impact on pregnancy outcomes, emphasizing the need for genetic compatibility and counseling in knowing and treating potential hazards to fetal health.
Maternal Health and Its Impact on Early Pregnancy
Maternal health has a significant impact on embryo and fetal development during early pregnancy, affecting both growth and survival. Nutrition, chronic illnesses, lifestyle choices, and prenatal care are all factors affecting fetal development that have a substantial impact on the developing embryo’s health.
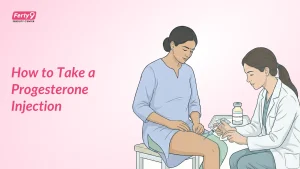
Hormonal Balance and Progesterone Levels
Hormonal balance, especially progesterone levels, is important for fetal development. Low progesterone levels can lead to a thin uterine lining, increasing the risk of pregnancy complications, including first-trimester miscarriage, and it becomes difficult to maintain a pregnancy. High levels can cause ligaments and joints to loosen, which can increase the risk of sprains and strains and make internal structures, like the ureters, increase in size. Therefore, the imbalance in the hormonal level can lead to complications like diabetes, premature birth, miscarriage, and low birth weight.
Pre-existing Conditions (e.g., Diabetes, PCOS)
The fetal health and the mother’s health can be greatly impacted by pre-existing diseases such as diabetes and PCOS during the early stages of pregnancy. These illnesses are more likely to cause complications like miscarriage, congenital defects, and gestational hypertension. Early intervention and appropriate care are essential for a successful pregnancy.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Their Effects
Nutritional deficiencies during early pregnancy, such as a lack of folic acid, iron, or iodine, can impair fetal and embryo development and increase the risk of neural tube defects, anemia, and developmental delays; however, adequate maternal nutrition is critical to support fetal healthy growth and reduce pregnancy-related complications.
Also Read: Top Vitamins for Boosting Fertility: A Comprehensive Guide
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Embryonic Growth
Lifestyle factors influencing fetal growth, l ike smoking, alcohol consumption, drug use, and high-stress levels, can all have a deleterious impact on embryonic growth, resulting in developmental delays and difficulties. Adopting a healthy lifestyle throughout early pregnancy is critical for good fetal growth. Eating a balanced diet, including fruits, vegetables, and grains, can improve embryo quality.
Smoking, Alcohol, and Drug Use
Smoking during pregnancy reduces oxygen availability to the embryo, resulting in low birth weight, premature birth, and developmental problems. Alcohol intake can result in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD), which are characterized by physical abnormalities and cognitive impairment. Drug abuse can disturb normal fetal and embryonic development, raising the risk of congenital abnormalities, growth limits, and pregnancy loss.
Stress and Its Impact on Pregnancy
Due to the numerous changes that occur throughout pregnancy, feeling stressed is quite normal. However, stress during pregnancy can increase the likelihood of having a preterm baby (born before 37 weeks) or a low-birthweight baby. Long-term stress can lead to health issues such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
The Role of Physical Activity
During pregnancy, exercise has a major positive impact on both the fetal health and the mother’s health. Normal-weight women with singleton, uncomplicated pregnancies did not have a higher risk of preterm births or low-birth-weight babies if they engaged in aerobic and moderate-intensity strength/toning training three or four days a week during their pregnancy. Pregnancy-related exercise has been proven to reduce urine incontinence, low back discomfort, pelvic girdle pain, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, macrosomia, and cesarean birth.
Environmental Influences on Early Embryonic Development
Modest environmental changes (such as dietary adjustments or exposure to toxins) or adjustments to the mother’s homeostasis can impact the uterine environment, altering the composition of the uterine fluid (i.e., amino acids), which can impact the embryo and its epigenetic state and cause changes later in life.
Exposure to Toxins and Pollutants
Several environmental toxins can affect an embryo, fetus, or infant as they are developing. Heavy metals, pesticides, and air pollution are just a few examples of the toxins and pollutants that might disrupt embryonic and fetal development and cause birth abnormalities, developmental delays, or pregnancy difficulties. Reducing exposure to the environmental toxins is crucial in protecting the health of both the mother and the fetus.
Also Read: How Does the Uterine Environment Affect Embryo Health?
Workplace Hazards and Precautions
Early embryonic development, fertilization, and embryo implantation can all be hampered by exposure to specific chemicals, pathogenic agents, and physical elements in the workplace. Protecting maternal and fetal health requires implementing safety measures and making sure the workplace is supportive.
Medical Interventions That Support Healthy Development
Having a healthy pregnancy is one of the most effective methods to ensure a healthy birth. Early and frequent prenatal care increases the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy. Women can have a healthy pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby by taking the next steps before becoming pregnant:
- Increase their daily dose of folic acid to at least 400 micrograms.
- Ensure that the vaccines are up to date.
- Manage diabetes and other medical disorders.
- Avoid smoking, consuming alcohol, and taking drugs.
- Achieve a healthy weight.
Prenatal Vitamins and Folic Acid
Taking 400 micrograms of folic acid daily lowers the incidence of neural tube abnormalities by 70%. Most prenatal vitamins have the recommended 400 micrograms of folic acid, as well as additional vitamins that pregnant women and their developing fetuses require. Foods containing folic acid include cereals, breads, pasta, and other grain-based foods.
Regular Prenatal Checkups
Early, regular prenatal care raises the odds of having a healthy pregnancy. This care can begin before pregnancy with a visit to a health care practitioner. They can help to lower the risk of problems and guarantee a safe delivery.
Common Risks and Challenges in Early Pregnancy
Some women have health issues while pregnant. These complications may affect the mother’s health, the fetus’s health, or both. Even women who were healthy before becoming pregnant may encounter health difficulties. Early and regular prenatal care can help to lower the risk of complications by allowing healthcare practitioners to diagnose, treat, or manage disorders before they worsen. Prenatal care can also assist in discovering mental health issues associated with pregnancy, such as anxiety and depression.
Threatened Miscarriage
Miscarriage refers to the loss of a pregnancy due to natural reasons before the 20th week. Signs include vaginal spotting or bleeding, cramps, and the passage of fluid or tissue from the vagina. Women encountering this indication at any time during their pregnancy should contact their healthcare practitioner.
Also Read: Six Steps to Prepare for Pregnancy Following a Miscarriage
Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is one that occurs outside of the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This is also called a tubal pregnancy. Almost all ectopic pregnancies —more than 90%—occur in the fallopian tubes. As the pregnancy progresses, the tube could rupture. A rupture might lead to extensive internal bleeding.
Abnormal Embryonic Development
Abnormal embryonic development, often known as congenital abnormalities or birth defects, can occur at any point during development. These anomalies may appear in any portion of the body, including the bones and organs. The three basic categories in which developmental defects can emerge are genetic (inherited), environmental (maternal), and idiopathic (unknown, undetermined) generated abnormalities.
Tips for Ensuring Healthy Embryonic Development
You can ensure good embryonic development by
- Balanced diet
- Regular physical exercise
- Having more water
- Regular Prenatal care
- Prenatal vitamins and folate
- Avoid excess caffeine and alcohol
- Quit smoking
- Avoid harmful substances and exposure
- Emotional and mental wellness
Conclusion
To summarize, pregnancy and embryonic development are impacted by genetic, maternal, environmental, and lifestyle variables. Understanding and regulating these factors is critical for promoting healthy growth and minimizing the chance of problems. Early interventions, excellent care, and a supportive environment are important for ensuring healthy fetal development.