Reviewed By: Dr. G Poornima, fertility specialist at Ferty9 Fertility Center, Karimnagar
Have you ever wondered how modern medicine can help men who struggle with infertility? Enter the world of sperm retrieval techniques – a groundbreaking field that’s changing lives. In this blog, we’ll demystify PESA, TESE, and Micro-TESE, three cutting-edge procedures that are offering hope to couples facing male factor infertility. Let us discover how these procedures are revolutionizing fertility treatment.
What are Sperm Retrieval Procedures?
Sperm retrieval procedures are specialised medical techniques used to take out sperm directly from your testicles or epididymis- the small, coiled tube that stores and transports sperm. These procedures are typically employed when a man is unable to produce sperm through natural ejaculation, a condition known as azoospermia.
Various factors, including genetic disorders, hormonal imbalances, previous surgeries, or obstruction in the reproductive system, can cause azoospermia. In such cases, sperm retrieval techniques offer hope for couples struggling with infertility, as the extracted sperm is a viable option for assisted reproductive technologies (ART), like intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
The decision to undergo a sperm retrieval procedure is often a complex one, requiring careful consideration of the individual’s medical history, the underlying cause of azoospermia, and the potential risks and benefits of each technique. Working closely with a fertility specialist is vital to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
The Timing of Sperm Retrieval
The timing of sperm retrieval is a crucial factor in the success of these procedures. Typically, sperm retrieval is scheduled in coordination with the female partner’s fertility cycle, ensuring that the retrieved sperm can be used for immediate fertilisation or cryopreservation for future use.
In some cases, doctors may perform sperm retrieval in advance and store and freeze the extracted sperm for later use. This approach can be beneficial for people who are taking treatments that may affect their fertility, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Which Sperm Retrieval Procedure is Recommended?
Each Sperm Retrieval Procedure has its own advantages, disadvantages, and success rates, and you should decide after consultation with a fertility expert.
Related Read: Why Dropping One’s Tobacco Habit is Important for Male Infertility?
These are some common sperm retrieval procedures:
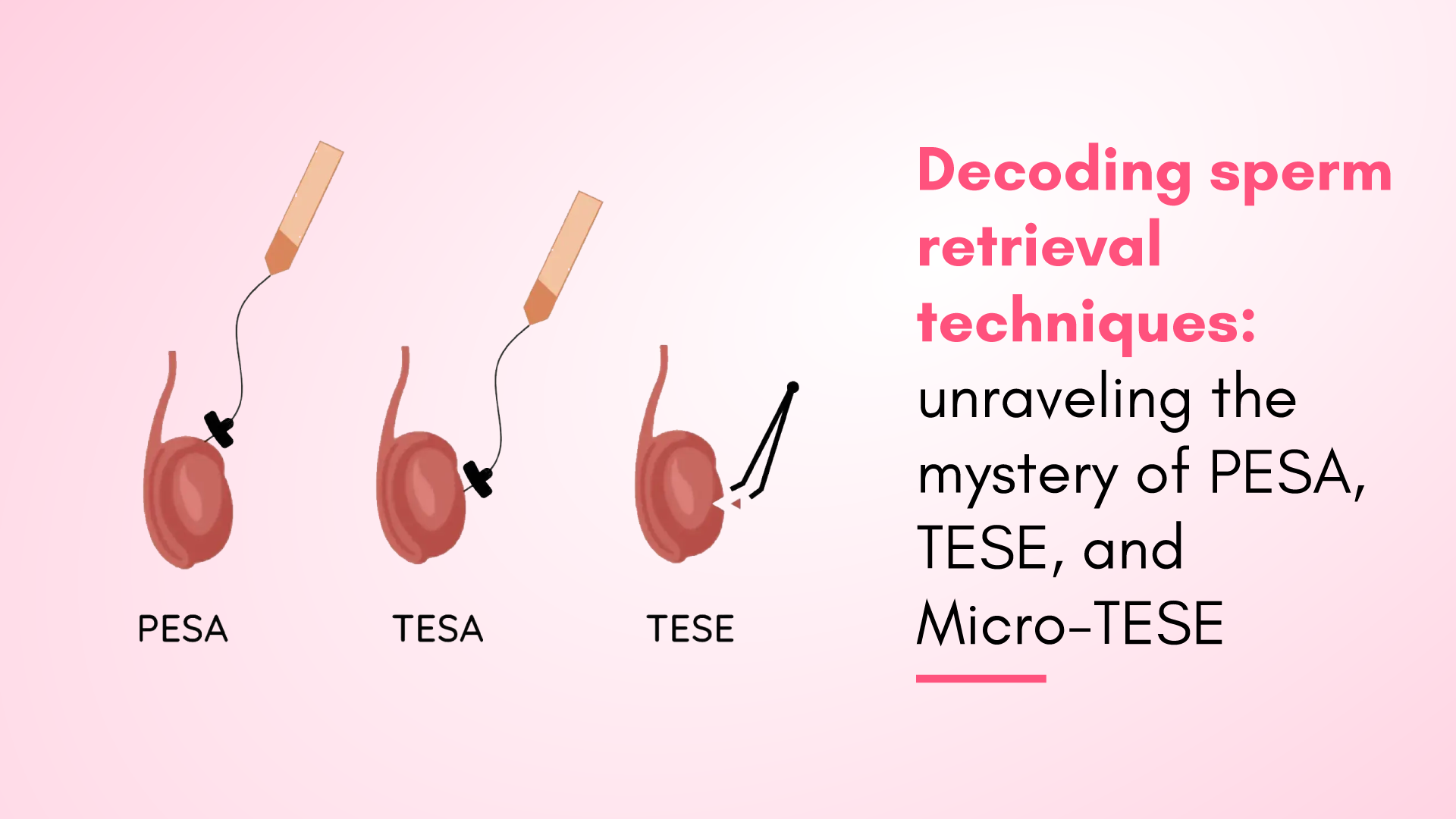
1. Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA):
Testicular sperm aspiration (TESA) is a procedure which causes no to minimal tissue damage. In this procedure, a thin needle extracts sperm directly from the testicles. This technique is often the first-line approach for men with non-obstructive azoospermia, where the testicular tissue is unable to produce sperm naturally.
During the TESA procedure, the fertility specialist numbs the area around the testicle and then inserts a small needle to aspirate (or withdraw) a sample of testicular tissue. Your doctor then examines the extracted sample under a microscope and determines the presence and quality of the sperm.
TESA is a relatively simple and quick procedure. Its success rate ranges from 30% to 50% in men with non-obstructive azoospermia (abesnce of sperm in the semen due to issues with sperm production). It is generally painless, with minimal discomfort and a low risk of complications.
Related Read: Fertility and Nutrition: Foods and Supplements That May Boost Male Fertility
2. Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (PESA):
Percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA) is a sperm retrieval technique used to retrieve sperm from the epididymis. This procedure is recommended for men with obstructive azoospermia, where the blockage is located in the reproductive tract, preventing sperm from being ejaculated.
During a PESA procedure, the fertility specialist numbs the area around the epididymis and then inserts a small needle to aspirate a sample of sperm. The extracted sperm can then be used for ARTs (assisted reproductive technologies), such as IVF or ICSI.
PESA is a minimally invasive procedure with a success rate of around 60% to 80% in men with obstructive azoospermia. It is generally well-tolerated, with a low risk of complications, and is an outpatient procedure.
3. Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE):
Testicular sperm extraction (TESE) is a more invasive procedure in which the fertility specialist surgically removes a small sample of testicular tissue to retrieve sperm. Doctors generally recommend this technique for men with non-obstructive azoospermia, where the testicular tissue is unable to produce sperm naturally.
During a TESE procedure, the fertility specialist makes a small incision in the scrotum and removes a small sample of testicular tissue. The extracted testicular tissue is then examined under a microscope to determine the presence and quality of the sperm.
TESE has a success rate of around 50% to 60% in men with non-obstructive azoospermia. While it is a more invasive procedure than TESA or PESA, it can be an effective option for men who have not responded to other sperm retrieval techniques.
Also Read: IVF cost – Myths and facts, inclusions, Ferty9’s promise of affordability
4. Microepididymal Sperm Aspiration (MESA):
Microepididymal sperm aspiration (MESA) is a specialised technique used to retrieve sperm from the epididymis under the guidance of a microscope. Doctors generally recommend this procedure for men with obstructive azoospermia, where the blockage is present in the reproductive tract.
During a MESA procedure, the fertility specialist makes a small incision in the scrotum and, with the help of a microscope, locates and aspirates sperm from the epididymis and uses them for assisted reproductive technologies (IVF or ICSI).
MESA is a more complex procedure than PESA, with a success rate of around 70% to 90% in men with obstructive azoospermia. Highly skilled fertility specialists generally perform it with extensive experience in microsurgical techniques.
Also Read: How to increase sperm count and motility
5. Microdissection TESE (microTESE):
Microdissection TESE (microTESE) is a specialised surgical technique used to retrieve sperm from the testicular tissue. This procedure is recommended for men with non-obstructive azoospermia, where the testicular tissue is unable to produce sperm naturally.
During a microTESE procedure, the fertility specialist makes a small incision in your scrotum and, using a microscope, dissects and removes small samples of testicular tissue carefully. The sample tissues are then examined under a microscope to identify and retrieve any viable sperm.
MicroTESE is a more complex and delicate procedure than traditional TESE. It has a success rate of around 50% to 70% in men with non-obstructive azoospermia. Highly skilled fertility specialists generally perform it with extensive experience in microsurgical techniques.
Related Read: Expectations of Microscopic Treatment for Male Infertility
Conclusion
Sperm retrieval procedures play a crucial role in the management of male infertility, particularly in cases of azoospermia. Each technique, from TESA and PESA to TESE, MESA, and microTESE, has its own unique advantages and considerations. The appropriate procedure choice depends on the underlying cause of azoospermia, the individual’s medical history, and the expertise of the fertility specialist.
By understanding the various sperm retrieval techniques and their respective benefits and limitations, couples struggling with infertility can make informed choices and work closely with their fertility experts to explore the best course of action for their specific situation.
Visit Our Clinic:
Fertility Clinic in Hyderabad
Fertility Clinic in Visakhapatnam
Fertility Clinic in Vijayawada
Fertility Clinic in Warangal
Fertility Clinic in Rajahmundry
Fertility Clinic in Tirupati
Fertility Clinic in Kurnool