Reviewed By: Dr. G Poornima, fertility specialist at Ferty9 Fertility Center, Karimnagar
The menstrual cycle in a woman’s body is a natural process that occurs every month to prepare for pregnancy. Menstruation begins during puberty and ends with menopause. The cycle usually lasts 28 days but can range from 20 to 35 days. The cycle duration is measured from the first day of bleeding in one cycle to the first day of bleeding in the following cycle. The cycle begins when the egg from the preceding menstrual cycle is not fertilized. Hormone levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease. The thicker uterine lining will degrade and shed since it is no longer needed. During the menstrual period, both the lining and the egg exit the vagina.
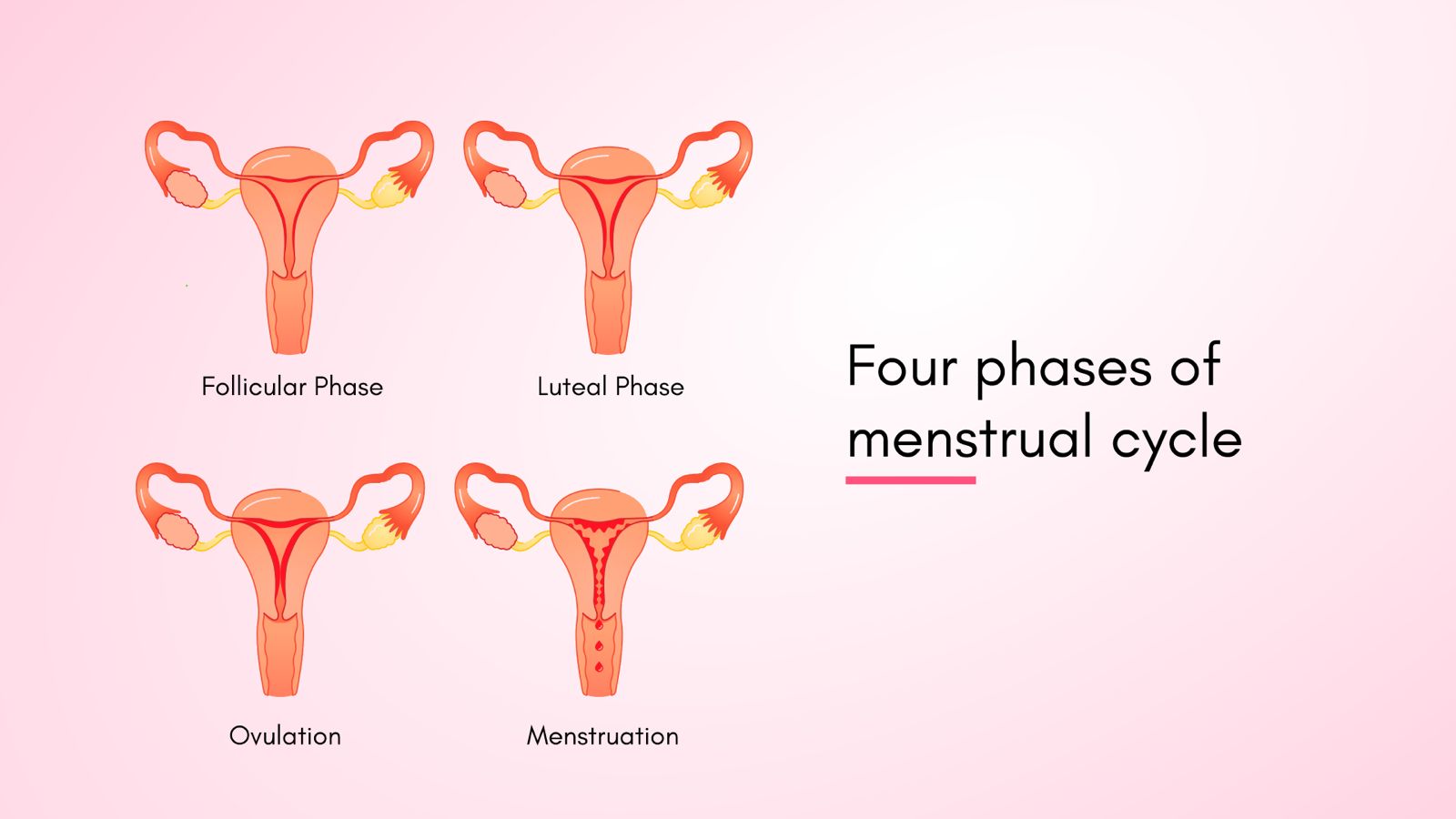
The menstrual cycle typically begins between ages 8 and 15, with an average age of 12. There are four phases in the menstrual cycle, and they are:
- Menstrual phase
- Follicular phase
- Ovulation phase
- Luteal phase
1. Menstrual Phase
Menstruation is the process of eliminating the uterine lining and other bodily fluids through the vagina. The period consists of uterine tissue, mucus, and blood. The duration typically ranges from three to eight days but may vary from month to month, depending on each woman’s health condition. During this phase, women can experience mood swings, tiredness, back pain, breast soreness, headaches, and abdominal cramps.
2. Follicular Phase
The follicular phase usually begins on the first day of bleeding and ends with ovulation. The follicular phase typically lasts between 10–16 days. During this period, the pituitary gland at the base of the brain produces a hormone that stimulates follicles. The follicular phase is described as the growth of ovarian follicles (10-20 follicles), which are fluid-filled structures that contain one egg each. Typically, only one follicle grows and gets to the ovarian surface, while the rest fade and are absorbed back into the body. The estrogen hormone level rises in this phase and plays a vital role in the thickening of uterine walls.
The most fertile time lasts from the three days before ovulation to the day of ovulation. This is also known as the “fertile window.”
3. Ovulation Phase
The ovulation phase begins when estrogen levels rise, causing the pituitary gland to generate luteinizing hormone (LH). LH promotes the process by which the ovary releases a mature egg. This procedure is known as ovulation. During ovulation, the developed egg moves from the ovary down through the fallopian tube and into the uterus, and sperm can fertilize an egg at any time during its journey. Ovulation usually takes place in the middle of the menstrual cycle. The egg can exist for around 24 hours before being fertilized. If the egg is not fertilized within this time, it will disintegrate.
Suggested Read:
Focused on Fertility: Natural Ways to Increase Ovulation
5 Tips for How to Increase Ovulation Naturally
4. Luteal Phase
The final phase of the menstrual cycle is called the luteal phase. In this phase, the follicle that produces the mature egg, known as the yellow body of the ovary or corpus luteum, releases a significant amount of progesterone and estrogen, which keeps the uterine membrane thick and prepared for a fertilized egg to implant.
- The body produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) if an egg is fertilized. hCG helps to maintain the uterine lining, allowing the fertilized egg to become an embryo.
- However, if the egg is not fertilized during ovulation, the corpus luteum dissolves into the body. The menstrual period begins when estrogen and progesterone levels decline.
The duration of the luteal phase varies, although it typically lasts around 14 days. During the luteal phase, a person may suffer symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Hormonal Influences Throughout the Cycle
All hormones in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis increase in one phase of the menstrual cycle and decrease in the other phase. All of these shifts have an impact on ovulation and can produce symptoms such as acne, low mood, headaches, weight gain, bloating, and appetite changes.
Factors Affecting the Menstrual Cycle
Several factors might impact your cycle, causing abnormalities or even missing a month of your menstrual cycle.
- Lifestyle factors (stress, diet, physical activity, sleep)
- Disease and medications (hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders)
- Endometriosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Uterine fibroids
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Geographic factors (temperature, humidity, latitude, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation)
- Intrauterine and childhood factors
Tracking and Understanding Your Cycle
Start tracking your menstrual cycle on a calendar to see what’s typical for you. Begin by noting your start date every month for several months to determine the frequency of your periods. While tracking periods, you should take note of the end date, flow, discomfort or cramps, mood swings, bleeding variations, or any other changes during the menstrual cycle.
Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
It’s impossible to say when ovulation occurs, although most women experience it between 10 and 16 days before their next period. Women with a typical 28-day cycle are more likely to be fertile around day 14 of their menstrual cycle, but this does not apply to those with shorter or longer periods.
Conclusion
Each menstrual cycle is unique. Some people receive their period around the same time every month. Others are more irregular. Some bleed more profusely or for longer periods of time than others. Your menstrual cycle might also fluctuate at specific points in your life due to several factors. It’s critical to become familiar with your cycle, including when you receive your periods and how long they last. Beware of any changes in your menstrual cycle, and contact a healthcare professional immediately.
Visit Our Clinic:
Fertility Clinic in Hyderabad
Fertility Clinic in Visakhapatnam
Fertility Clinic in Vijayawada
Fertility Clinic in Warangal
Fertility Clinic in Rajahmundry
Fertility Clinic in Tirupati
Fertility Clinic in Kurnool