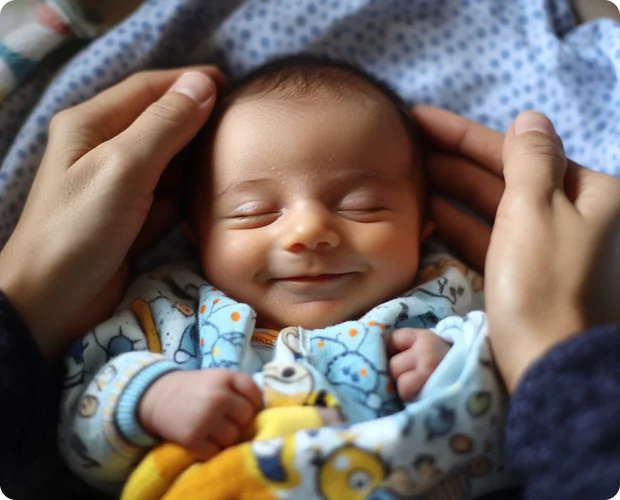
As hopeful parents, we all dream of giving our children the best start in life. One important step towards that is understanding genetic testing, which helps us ensure our little ones are born healthy.
Genetic testing examines changes in genes, genomes, and proteins to detect potential chromosomal abnormalities. It identifies DNA sequences and mutations that may cause genetic disorders.
Why Genetic Testing and Screening Matters?
Initially, genetic testing was common among couples with a family history of genetic disorders. Today, this test is recommended for all couples to help rule out genetic disorders in newborns. Contrary to popular belief, this screening is not just for the mothers. Pre-pregnancy tests for males are as important as for females!
How Is Genetic Testing Performed?
Genetic testing involves analyzing an individual’s blood, skin, hair, or other body tissue to look at his or her DNA, chromosomes, or proteins for a change or mutation that is associated with a genetic condition. When a mutation occurs, it may affect all or part of a gene and can result in an abnormal function, leading to disease. Three major types of genetic testing are available in laboratories: cytogenetic (to examine whole chromosomes), biochemical (to measure protein produced by genes), and molecular (to look for small DNA mutations).
Before starting your family journey, here’s what you should know about this testing:
Prenatal Genetic Testing and Analysis
Prenatal Genetic Testing checks for chromosomal abnormalities or other genetic diseases the fetus may inherit. It commonly screens for conditions such as sickle-cell disease, Down syndrome, and cystic fibrosis.
Chromosomal abnormalities, such as aneuploidy, involve missing or extra chromosomes. Monosomy refers to a fetus missing a chromosome, whereas trisomy indicates an extra chromosome.
After conducting prenatal tests, genetic counselors carefully analyze the results. They provide comprehensive information and emotional support to help expectant parents make informed decisions.
It’s important to note that while some genetic abnormalities are serious, many can be effectively managed with appropriate treatments and interventions.
Suggested Read: Genetic Testing Costs in Fertility Treatment: PGS/PGT
Identifying Genetic Abnormalities
Understanding genetic abnormalities can seem overwhelming, but it’s a vital step in ensuring your baby’s health. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of genetic tests, explained in a way that’s easy to understand:
- Preimplantation Genetic Tests:
- PGT-A (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidies): Screens embryos for chromosomal abnormalities, selecting the most viable ones for implantation.
- PGT-M (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic/Single Gene Disorders): Targets specific genetic mutations to ensure embryos free from certain hereditary conditions are selected.
- PGT-SR (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Structural Rearrangements): Analyzes embryos for structural chromosomal issues to identify genetically balanced ones.
- Presymptomatic and Predictive Testing: For those with a family history of genetic disorders, this testing can indicate the risk of developing conditions like certain types of colorectal cancer before symptoms appear.
- Carrier Testing: Carrier testing can be used to help couples learn if they carry—and thus risk passing to their children—an allele for a recessive condition such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease. This type of testing is typically offered to individuals who have a family history of a genetic disorder and to people in ethnic groups with an increased risk of specific genetic conditions. If both parents are tested, the test can provide information about a couple’s chance of having a child with a genetic condition.
- Prenatal Testing: For expecting parents, this testing identifies genetic abnormalities in the fetus, such as Down syndrome or trisomy 18, through blood markers or invasive procedures like amniocentesis.
- Newborn screening is the most widespread use of genetic testing. Almost every newborn in the U.S. is screened for several genetic diseases. Early detection of these diseases can lead to interventions to prevent the onset of symptoms or minimize disease severity.
By understanding these tests, you’re taking an important step in safeguarding your child’s health. Genetic counselors help you make sense of the results and support you in making the right choices.
Genetic Screening During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, genetic screening helps us ensure our baby’s health right from the start. It involves a series of tests that look for any potential genetic abnormalities. This may involve a fetal ultrasound and a maternal blood test in the first trimester. In the second trimester, additional blood tests, known as multiple markers, are conducted to check for genetic abnormalities or birth defects. Other tests include amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Throughout your pregnancy, regular check-ups include fetal monitoring to track your baby’s growth and development. Tests like group B strep culture are also done to ensure everything stays healthy.
Remember, these tests are designed to give you peace of mind and help us take the necessary steps to ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Benefits and Limitations of Genetic Testing
Understanding the benefits and limitations of genetic testing is crucial for every parent-to-be. Here’s a straightforward take on what it can offer:
Since babies inherit 50% of their genetic material from each parent, checking for any conditions that might cause serious complications is vital.
Genetic testing not only detects genetic abnormalities in your child but also teaches us about the recessive traits that you might have and can manifest in the next generations.
While genetic testing provides valuable insights, it’s not without limitations. It can’t predict every possible health issue, and results may not always be definitive. Genetic counselors are invaluable in helping us navigate this information.
Genetic Testing and Treatment Options
When it comes to genetic testing, the goal is not just to detect issues but also to understand how to manage or treat them. Treatment options can vary widely depending on the situation.
Treatment for genetic abnormalities can range from medications to fetal interventions, depending on the complications. Genetic testing and counseling help determine if these conditions can be managed or treated with long-term care.
Remember, genetic testing is about empowerment—it gives us the tools to take proactive steps towards a healthy future for our children.
Genetic Counseling for Pregnancy
Genetic counseling is like having a roadmap to understand your family’s genetic story and how it could impact your baby’s health. Even if you haven’t faced any issues, it helps uncover potential genetic risks. This insight is crucial for ensuring your baby’s health right from the start.
Here are some common indicators that might suggest a need for genetic testing:
Red Flags of a Genetic Disease:
- Occurrence of a condition among family members revealed in the family history
- Occurrence of the condition in more than one family member, especially first-degree relatives
- Multiple miscarriages
- Stillbirths
- Childhood deaths
- Clinical symptoms that are suggestive of a genetic disease, like developmental delay or mental retardation
- Congenital abnormalities or physical features that appear unique or slightly different than the average, such as wide-set or droopy eyes, flat face, short fingers, and tall stature
After identifying potential risks, genetic testing can provide more clarity. After the tests, the genetic counselor will review the results with you. They provide clear explanations and discuss suitable options for managing any genetic findings. This helps you make informed choices for your family’s future.
It’s not just for those with a family history of diseases. If you’re over 35, having first cousins as relatives or experiencing multiple miscarriages or stillbirths—increases the likelihood of genetic abnormalities in your baby. Therefore, genetic counseling is highly recommended for individuals with these risk factors.
Conclusion
Genetic testing before and during pregnancy is vital for preventing genetic disorders in newborns. These tests detect genetic abnormalities early, helping to identify carrier status and providing essential genetic counseling for a healthy pregnancy. If any issues are found during pregnancy, many can be managed and treated effectively. Remember, a successful pregnancy requires more than conception—it involves staying informed and taking proactive steps for your health and your baby’s well-being.
If you have questions about genetic testing or need guidance on family planning, our fertility expert is here to help. Reach out today and empower yourself with knowledge for a healthier tomorrow.



























 No need to worry, your data is 100% safe with us!
No need to worry, your data is 100% safe with us!