Reviewed By: Mr. Sandeep Sharma, Head of Embryology at Ferty9 Fertility Center
This journey takes on a whole new meaning for couples navigating the complex world of in vitro fertilisation (IVF). At the heart of many successful IVF treatments lies a fascinating process known as blastocyst culture.
Imagine a tiny cluster of cells, barely visible to the naked eye, holding the potential for new life. This is a blastocyst—a critical stage in early embryo development that occurs about 5-6 days after fertilisation. Blastocyst culture is the careful nurturing of these delicate embryos in a laboratory setting, mimicking the conditions they would experience in a mother’s womb.
For those on the emotional rollercoaster of fertility treatment, understanding blastocyst culture can offer a glimmer of hope. It’s a process that allows embryologists to select the most viable embryos, potentially increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
But what exactly happens during these crucial days of development? How does blastocyst culture differ from traditional IVF methods? And most importantly, how might this advanced technique impact your fertility journey? Let’s explore these questions.
What is Blastocyst Culture?
In the journey of in vitro fertilisation (IVF), the term “blastocyst culture” holds significant importance. It refers to the process of allowing embryos to develop in a controlled laboratory environment until they reach the blastocyst stage, which typically occurs five to seven days after fertilisation.
The blastocyst is a highly advanced stage of embryonic development. It consists of an outer cell layer called the trophectoderm, which will form the placenta, and an inner cell mass, giving rise to the embryo. Blastocyst culture aims to mimic the natural environment within the uterus, providing the optimal conditions for embryos to reach this critical stage before being transferred back into the intended mother’s womb.
By extending the culture period beyond the traditional cleavage stage (day three), embryologists can observe and select the most viable and genetically competent embryos for transfer, potentially increasing the possibility of a successful pregnancy.
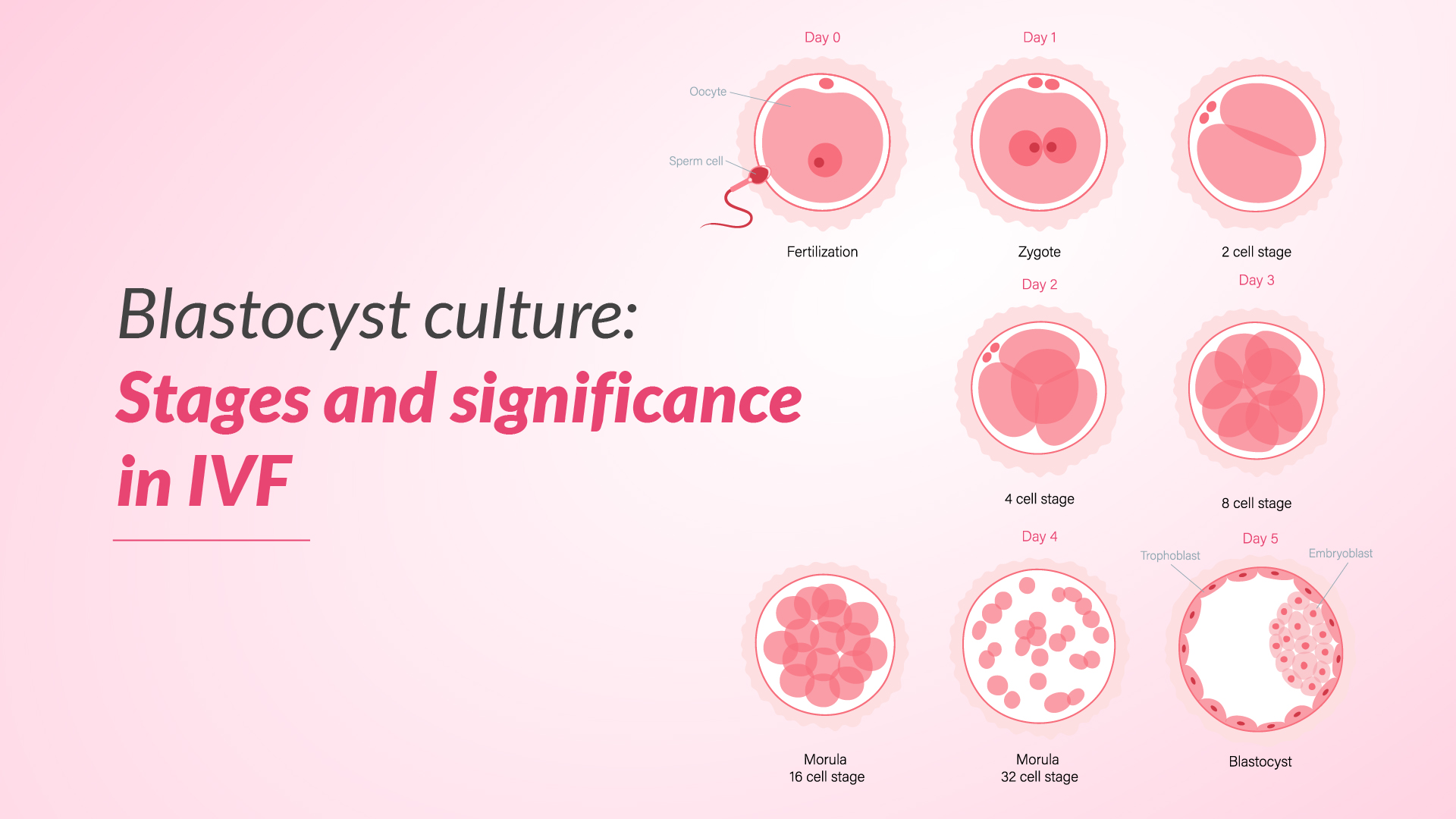
Stages of Blastocyst Development in Blastocyst Culture
The journey from fertilisation to the blastocyst stage is a remarkable process, with each stage playing a crucial role in the embryo’s development. Here’s a detailed look at the various stages:
Fertilisation (Day 0):
The process begins with the union of a sperm and an egg, forming a single-celled zygote. This marks the beginning of the embryo’s development and sets the stage for the subsequent stages.
Cleavage Stage (Days 1-3):
After fertilisation, the zygote goes through a series of rapid cell divisions known as cleavage. During this stage, the single-celled zygote divides into multiple cells, forming a compact ball of cells called the morula. These early cell divisions are crucial for the embryo’s development and provide insights into its potential for further growth.
Morula Stage (Day 4):
By day four, the embryo has reached the morula stage, consisting of 16 to 32 tightly compacted cells. At this stage, the cells begin to differentiate and organise themselves into two distinct cell lineages: the outer trophectoderm (which forms the placenta) & the inner cell mass (which gives rise to the embryo).
Early Blastocyst – Expanding Blastocyst Stage (Day 5):
On day five, the embryo enters the early blastocyst stage. During this phase, a fluid-filled cavity, known as the blastocoel, begins to form within the morula. This cavity separates the trophectoderm cells from the inner cell mass, creating a distinct structure resembling a hollow sphere.
Hatched Blastocyst Stage (Day 6 -7):
By day six, the blastocyst has significantly expanded, with the blastocoel increasing in size. The trophectoderm cells become more tightly packed, and the inner cell mass becomes more prominent. This stage is crucial for embryo selection, as the quality and development of the blastocyst can be assessed more accurately.
Implantation-Ready Blastocyst:
Once the blastocyst has reached the hatching stage, it is considered ready for implantation. At this point, the embryo has the potential to be successfully implanted in the uterine lining and continue its development into a healthy pregnancy.
Significance of Blastocyst Culture in IVF
The practice of blastocyst culture offers numerous advantages in the IVF process, contributing to improved outcomes and increased success rates. Here are some of the key benefits:
Extended Culture Period:
By allowing embryos to develop until the blastocyst stage, embryologists can observe their growth and development over an extended period. This can provide valuable insights into their viability and potential for successful implantation.
Natural Selection Process:
Blastocyst culture mimics the natural selection process that occurs within the uterus. Only the healthiest and most viable embryos can reach the blastocyst stage, allowing the selection of the best embryos for transfer.
Higher Pregnancy Rates:
Studies have shown that transferring blastocysts can lead to higher pregnancy rates than transferring embryos at earlier stages. This is because blastocysts have a higher implantation potential and are more likely to result in a successful pregnancy.
Reduced Risk of Multiple Pregnancies:
In traditional IVF cycles, multiple embryos are often transferred to increase the chances of pregnancy. This can lead to a heightened risk of multiple pregnancies, which can pose various health risks for both the mother and the babies. By selecting the best blastocysts for transfer, fewer embryos may be needed, reducing the risk of multiple pregnancies.
Enhanced Genetic Screening:
Blastocyst culture allows for more advanced genetic screening techniques, such as preimplantation genetic testing (PGT). These techniques can help identify embryos with genetic abnormalities or chromosomal disorders, increasing the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Better Synchronisation with Uterine Environment:
Blastocysts are more synchronised with the uterine environment, as they have reached a stage of development that closely mimics the natural process. This synchronisation can improve the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
Optimised Endometrial Receptivity:
By making embryos capable of developing to the blastocyst stage, the transfer can be timed to coincide with the optimal window of endometrial receptivity, when the uterine lining is most receptive to embryo implantation.
Improved Embryo Selection:
Blastocyst culture provides a more comprehensive evaluation of embryo quality, as the embryos have undergone additional developmental stages. It allows for selecting the most viable and genetically competent embryos, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Reduced Embryo Loss:
Compared to embryos transferred at earlier stages, embryos that reach the blastocyst stage enjoy a greater chance of successful implantation & a reduced risk of embryo loss.
Also read: Ferty 9 and its Blastocyst Culture and Transfer
10 Days After Blastocyst Transfer and Beyond, What to Expect?
After the blastocyst transfer, the journey continues, and there are several milestones to watch for:
- Implantation: If successful, the blastocyst will implant in the uterine lining approximately 6-10 days after the transfer. This process may cause light spotting or cramping, which is considered normal.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) Levels: Around 10-14 days after the transfer, doctors will conduct a blood investigation to measure the levels of hCG, a hormone produced by the placenta. Elevated hCG levels indicate a positive pregnancy.
- Ultrasound Scan: Approximately 4-6 weeks after the transfer, doctors will perform an ultrasound scan to visualise the presence of a gestational sac & heartbeat in the foetus, indicating a viable pregnancy.
- First Trimester: If the pregnancy progresses successfully, the first trimester will involve regular monitoring and follow-up appointments to ensure the healthy development of the embryo.
- Delivery: After a full-term pregnancy of approximately 40 weeks, the baby will be delivered, marking the culmination of the IVF journey.
It’s important to note that every pregnancy is unique, and the timeline may vary slightly for each individual. Patience, regular communication with your doctor, and adherence to recommended prenatal care are crucial during this exciting phase.
Also read: What to Avoid After Blastocyst Transfer?
Signs of Successful Blastocyst Transfer
While it’s essential to wait for the official confirmation from your doctor, certain signs and symptoms may indicate a successful blastocyst transfer:
- Implantation Bleeding: Light spotting or bleeding around 6-10 days after the transfer may be an early sign of implantation.
- Breast Tenderness: As pregnancy hormones begin to surge, breast tenderness or soreness can be an early indication of a positive outcome.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or exhausted can be a symptom of early pregnancy due to the hormonal changes occurring in the body.
- Nausea: Morning sickness, or nausea at any time of the day, can be an early sign of a successful pregnancy.
- Missed Period: If you were expecting your menstrual period and it didn’t arrive, it could be a positive sign that the blastocyst transfer was successful.
It’s important to remember that not all women experience these symptoms; some may experience them even with an unsuccessful transfer. A blood investigation to measure hCG levels and an ultrasound scan is the most reliable way to confirm a successful pregnancy.
Also read: How Soon Can You Try IVF Again After a Failed Cycle?
Conclusion
Blastocyst culture has revolutionized the field of IVF by providing a more advanced and effective approach to embryo selection and transfer. By allowing embryos to develop until the blastocyst stage, embryologists can cull out the most viable and genetically competent embryos, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
This extended culture period mimics the natural selection process and provides valuable insights into embryo development, enabling better synchronisation with the uterine environment and optimised endometrial receptivity. Additionally, blastocyst culture reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies and allows for enhanced genetic screening techniques, further improving the overall success rates of IVF.
Visit Our Clinic:
Fertility Clinic in Hyderabad
Fertility Clinic in Visakhapatnam
Fertility Clinic in Vijayawada
Fertility Clinic in Karimnagar
Fertility Clinic in Warangal
Fertility Clinic in Rajahmundry
Fertility Clinic in Tirupati
Fertility Clinic in Kurnool