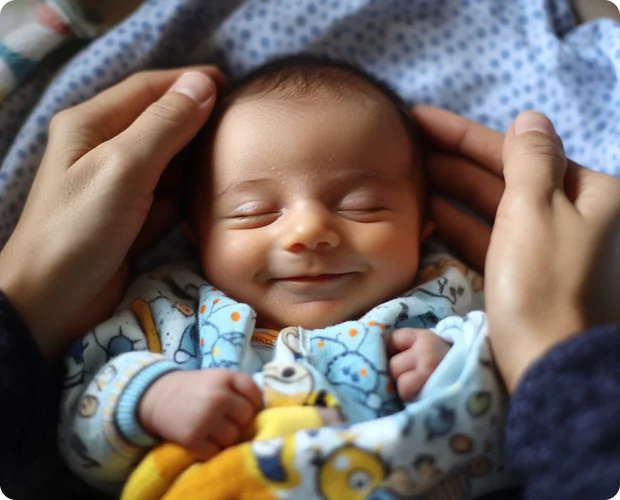
Are you considering birth control pills (BCPs) for their effectiveness in preventing pregnancy? While they offer both benefits and potential drawbacks, it’s essential to understand their impact on menstrual cycles and women’s health. Here’s everything you need to know about them and their effects.
How do Birth Control Pills Work?
Birth control pills (BCPs) contain synthetic versions of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. These hormones work together to suppress ovulation, the release of an egg from the ovaries. BCPs are highly effective in preventing pregnancy, with a failure rate of less than 1% per year with correct use.
Also Read: How to stop period’s pain?
Types of Birth Control Pills
There are two different types of birth control pills, which are as follows:
- Combination pills: These pills contain progestin and estrogen and prevent the ovaries from releasing eggs. They also thicken the cervical mucus and reduce the thickness of the uterine lining, which is called the endometrium.
- Minipill: Minipills contain only progestin. They primarily work by thickening the cervical mucus and thinning the uterine lining to prevent sperm from reaching eggs.
Effects on Menstrual Cycles
BCPs can significantly impact menstrual cycles, with both positive and negative effects:
- Regularization of Menstrual Cycle: It helps regulate irregular periods by stabilizing estrogen and progestin, thereby normalizing your menstrual cycle.
- Lighter and Shorter Periods: BCP stabilizes the uterine lining, leading to lighter and shorter periods by reducing tissue buildup shed during menstruation.
- Reduced Menstrual Pain: It can alleviate menstrual cramps by reducing the intensity of uterine contractions through hormonal effects.
- Spotting Between Periods: Some types of birth control pills may cause spotting between menstrual cycles (known as breakthrough bleeding). This is common when starting the pills and typically resolves within the first 3 months.
- Changes in Menstrual Symptoms: Birth control pills can affect premenstrual symptoms like mood swings, breast tenderness, and bloating. Responses to these changes vary among women.
Also Read: Tips for Maintaining Fertility While Pursuing a Fitness Passion
Impact on Fertility
Many women worry that using such pills to prevent pregnancy might affect their fertility in the future. It’s important to understand that birth control pills will not cause infertility when you stop using them. In rare cases, it may take up to three months for your normal menstrual cycle to resume after discontinuing the pills. This delay is usually temporary and does not indicate long-term fertility issues.
Rest assured, if you’re considering using birth control pills, they are generally safe and effective, and they do not impact your ability to have children in the future. If you have any concerns about fertility or starting and stopping the pills, speaking with your healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance and reassurance.
Suggested read: Female Infertility: Common Causes and Possible Solutions
Benefits Beyond Contraception
While contraception is their main purpose, BCPs have several other benefits:
- Relieve endometriosis and prevent ovarian cysts: BCPs manage endometriosis symptoms by suppressing menstruation, which can significantly alleviate associated pain. They also prevent the formation of functional ovarian cysts by inhibiting ovulation and stabilizing hormone levels, though it’s important to note that not all cyst types are impacted.
- Reduce anemia: BCPs can reduce heavy bleeding during menstruation and help individuals with anemia by minimizing blood loss.
- Improves skin: Skin conditions like acne or hair growth on your upper lips can be a result of hormonal imbalance in your body. BCPs regulate such imbalances and improve your skin.
- Bone Health: Some birth control pills may contribute to better bone density due to their hormonal effects.
Potential Side Effects
The most common side effects of birth control pills include:
- Tender breasts: Your breasts might get tender, sore, or enlarged when you’re on BCPs due to the excess amount of estrogen in them.
- Nausea: Some types of BCP can cause nausea in some people in the initial few days. However, this is generally mild and goes away on its own.
- Mood swings: Since BCPs contain synthetic estrogen and progestin, you might be subject to frequent mood swings that feel like PMS.
- Increases weight: These pills can retain fluid in your body and increase your weight by increasing muscle mass or fat.
- Headaches: Some individuals may experience headaches or migraines as a side effect.
- Decreased Libido: In some cases, it may affect sexual desire.
- Blood Clot Risk: Certain types of birth control pills may slightly increase the risk of blood clots, especially in women who smoke or have other risk factors.
Not all women experience these side effects, and their severity can vary. Consulting a healthcare provider can help manage any concerns effectively.
Suggested Read: Six Steps to Prepare for Pregnancy Following a Miscarriage
Considerations for Women’s Health
While these pills are generally regarded as safe to consume, they might not be suitable for people with certain medical conditions. Hence, it is vital to consult with your healthcare professional to decide which types of BCPs are best for you.;
Alternative Birth Control Methods
Oral contraceptives aren’t the only way of preventing conception. There are several other options, like vaginal rings, intrauterine devices, and injections that can prevent pregnancy. Moreover, non-hormonal birth control methods like using a condom and having protective intercourse can reduce the chances of pregnancy by 98%.
Also Read: Fertility Challenges In PCOS: Strategies For Management And Treatment
Conclusion
Birth control pills offer reliable contraception, enabling you to plan pregnancy when the time is right. These hormonal methods, guided by healthcare professionals for safety, aim to transition from hope to happiness. Rest assured, they are generally safe and effective. Your healthcare provider can assist in choosing the best option for your needs, ensuring peace of mind in your reproductive choices.
If you have any questions or need personalized guidance, consult our fertility expert today to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.